AI for Medicine
A wealth of studies have demonstrated that Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) and Western medicine share the same theoretical foundation at the molecular level. However, current information on the chemical components and metabolism mechanisms of TCM remains insufficient, rendering the relationship between drug components and pharmacological effects unclear and thereby hindering targeted diagnosis and treatment. Although recent efforts have been made to construct databases that incorporate information on herbs, ingredients, and targets to support related research, these databases are often plagued by varying degrees of information loss. Specifically, existing databases tend to represent relationships in a binary manner, whereas biological processes are inherently complex and diverse.
Basic Idea:
- Aligning knowledge from multiple medicinal knowledgebases with large language model(LLM) to construct the most comprehensive medicinal database.
- Developing novel deep learning models to mine implicit information within medicinal data, supporting researches of prescription generation, knowledge discovery, and bioactive constituent identification.
Identification of bioactive constituents for colitis from traditional Chinese medicine prescription via deep neural network
Paper Link: https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.05.31.542690.abstract
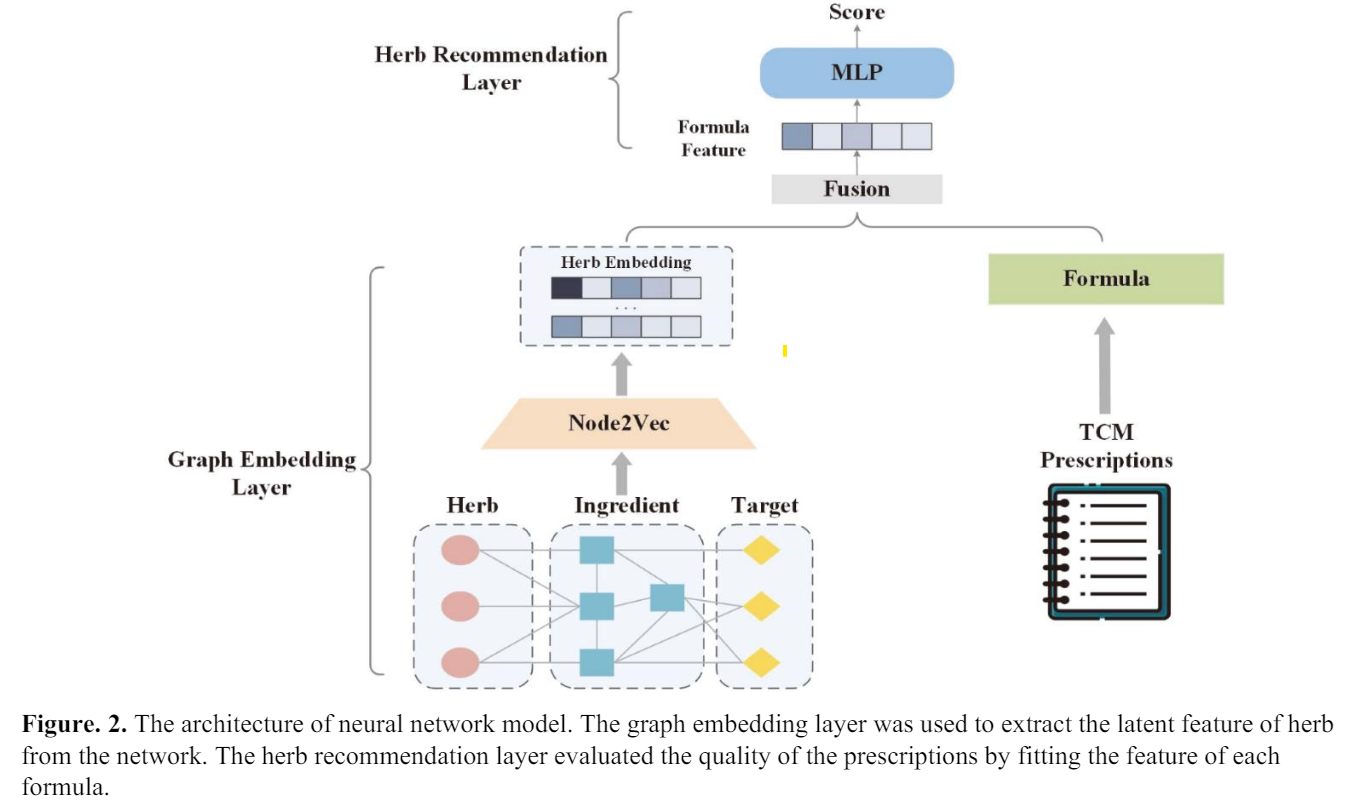
Colitis is a commonly encountered inflammatory disease in colon tissue, which can be triggered by various causes. Although traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been utilized for the treatment of colitis, it is still a great challenge to identify the major bioactive constituents and their modes of action among thousands of ingredients in TCM prescriptions. Inspired by the success of artificial intelligence and deep learning methods, we proposed a deep neural network (DNN) for TCM prescription recommendation. We constructed a graph-based DNN with 9,845 nodes and 161,950 edges, which integrated microscopic information including bioactive molecules, protein targets, and extracted features of prescriptions through feature embedding. A novel and efficient data augmentation strategy was implemented to expand the sample size based on 378 collected TCM prescriptions. Network pharmacology study revealed that the 10 most frequent ingredients in generated prescriptions were associated with multiple inflammatory signaling pathways. To verify the bioactive constituents in the generated prescriptions, 5 selected constituents were administrated to BALB/c mice with colitis. Suppressive effects of disease progression and proinflammatory factors comparable to sulfasalazin were observed with these compounds, revealing the effectiveness of our artificial intelligence strategy on idetification of bioactive constituents from TCM prescriptions.
TCMM: A Unified Database for Traditional Chinese Medicine Modernization and Therapeutic Innovations
Paper Link: https://www.csbj.org/article/S2001-0370(24)00105-3/fulltext
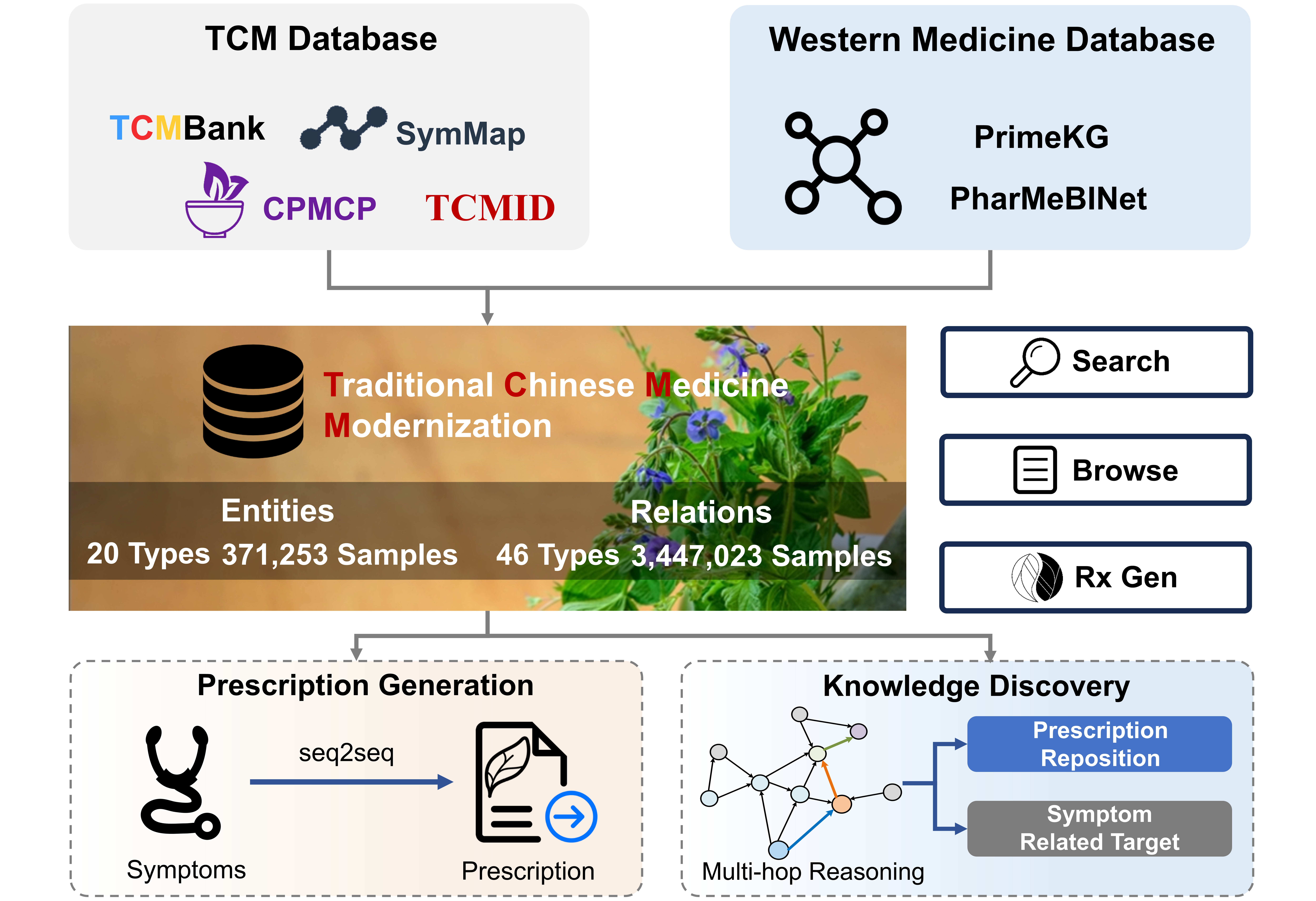
Mining the potential of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in treating modern diseases requires a profound understanding of its action mechanism and a comprehensive knowledge system that seamlessly bridges modern medical insights with traditional theories. However, existing databases for modernizing TCM are plagued by varying degrees of information loss, which impede the multidimensional dissection of pharmacological effects. To address this challenge, we introduce traditional Chinese medicine modernization (TCMM), the currently largest modernized TCM database that integrates pioneering intelligent pipelines. By aligning high-quality TCM and Western medicine data, TCMM boasts the most extensive TCM modernization knowledge, including 20 types of modernized TCM concepts such as prescription, ingredient, target and 46 biological relations among them, totaling 3,447,023 records. We demonstrate the efficacy and reliability of TCMM with two features, prescription generation and knowledge discovery, the outcomes show consistency with biological experimental results. A publicly available web interface is at https://www.tcmm.net.cn/.
